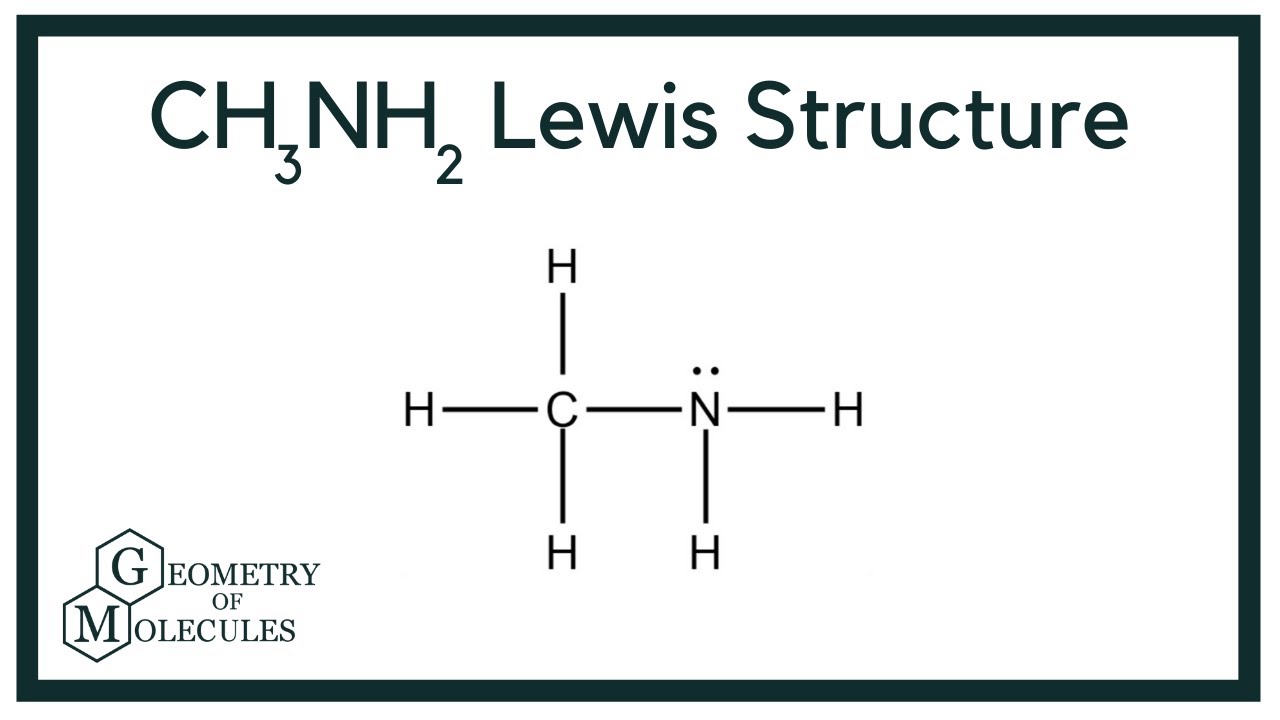
The CH3NH2 Lewis structure is an essential topic for chemistry enthusiasts and students alike, as it plays a crucial role in understanding molecular geometry and bonding characteristics. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the CH3NH2 Lewis structure, exploring its formation, significance, and applications in various chemical contexts. By the end of this guide, you will have a comprehensive grasp of how to represent and interpret this important molecular structure.
Understanding the Lewis structure is fundamental to grasping the behavior of molecules in chemical reactions and their interactions with other substances. The representation of CH3NH2, also known as methylamine, is particularly important in organic chemistry and biochemistry, as it serves as a building block for various biological and synthetic compounds. This article will provide you with a detailed breakdown of the CH3NH2 Lewis structure, its properties, and its relevance in the broader field of chemistry.
As we progress through this guide, we will highlight the key aspects of the CH3NH2 Lewis structure, including the arrangement of atoms, the distribution of valence electrons, and the overall molecular geometry. We will also address common questions and misconceptions surrounding this structure, ensuring that you leave with a well-rounded understanding of the topic. Let's get started!
Table of Contents
- What is CH3NH2?
- Importance of Lewis Structure
- Steps to Draw the CH3NH2 Lewis Structure
- Molecular Geometry of CH3NH2
- Properties of CH3NH2
- Common Applications of CH3NH2
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is CH3NH2?
CH3NH2, or methylamine, is a simple organic compound that consists of a methyl group (CH3) attached to an amino group (NH2). It is a colorless gas with an odor similar to ammonia and is highly soluble in water. Methylamine is classified as a primary amine due to its single nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms and one carbon atom.
Biographical Data of CH3NH2
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | CH3NH2 |
| Molecular Weight | 31.06 g/mol |
| Boiling Point | 6.3 °C |
| Melting Point | -93.5 °C |
Importance of Lewis Structure
The Lewis structure is a diagram that represents the arrangement of electrons in a molecule. It provides insight into the bonding patterns and molecular geometry, which are crucial for predicting the behavior of the molecule in chemical reactions. Understanding the CH3NH2 Lewis structure helps in various applications, including:
- Predicting reactivity and stability of the molecule.
- Understanding intermolecular forces and polarity.
- Facilitating the study of organic compounds and their derivatives.
Steps to Draw the CH3NH2 Lewis Structure
Drawing the CH3NH2 Lewis structure involves several systematic steps:
- Count the total valence electrons: Carbon (C) has 4, nitrogen (N) has 5, and hydrogen (H) has 1. Therefore, total valence electrons = 4 + 5 + (2 × 1) + (3 × 1) = 12.
- Identify the central atom: The carbon atom will be the central atom in the CH3NH2 structure.
- Arrange the surrounding atoms: Attach three hydrogen atoms and one nitrogen atom to the carbon atom.
- Distribute the remaining electrons: Place the remaining electrons around the nitrogen atom to complete its octet.
- Check the structure: Ensure that all atoms have a complete valence shell.
Molecular Geometry of CH3NH2
The molecular geometry of CH3NH2 can be described as trigonal pyramidal. The presence of a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom influences the shape of the molecule, causing the hydrogen atoms to be positioned at the corners of a pyramid with the nitrogen atom at the apex. This geometry has important implications for the molecule's reactivity and interactions.
Properties of CH3NH2
Understanding the properties of CH3NH2 is crucial for its applications in various fields. Some notable properties include:
- Solubility: CH3NH2 is highly soluble in water due to its polar nature.
- Basicity: Methylamine acts as a weak base, making it useful in organic synthesis.
- Reactivity: It can undergo various reactions, including alkylation and acylation.
Common Applications of CH3NH2
Methylamine is utilized in numerous applications, including:
- As a building block in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.
- In the production of surfactants and polymers.
- As a reagent in organic chemistry for various transformations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions related to the CH3NH2 Lewis structure:
- What is the hybridization of CH3NH2? The nitrogen atom in CH3NH2 is sp3 hybridized.
- Is CH3NH2 polar or nonpolar? CH3NH2 is a polar molecule due to the difference in electronegativity between nitrogen and hydrogen.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the CH3NH2 Lewis structure provides valuable insights into the molecular geometry and bonding characteristics of methylamine. Understanding this structure is essential for predicting the behavior of the molecule in various chemical contexts, making it a fundamental topic in chemistry. We encourage you to explore further and deepen your understanding of organic compounds and their properties.
Thank you for reading! If you found this article helpful, please consider leaving a comment, sharing it with your friends, or checking out our other articles on chemistry topics.
Article Recommendations