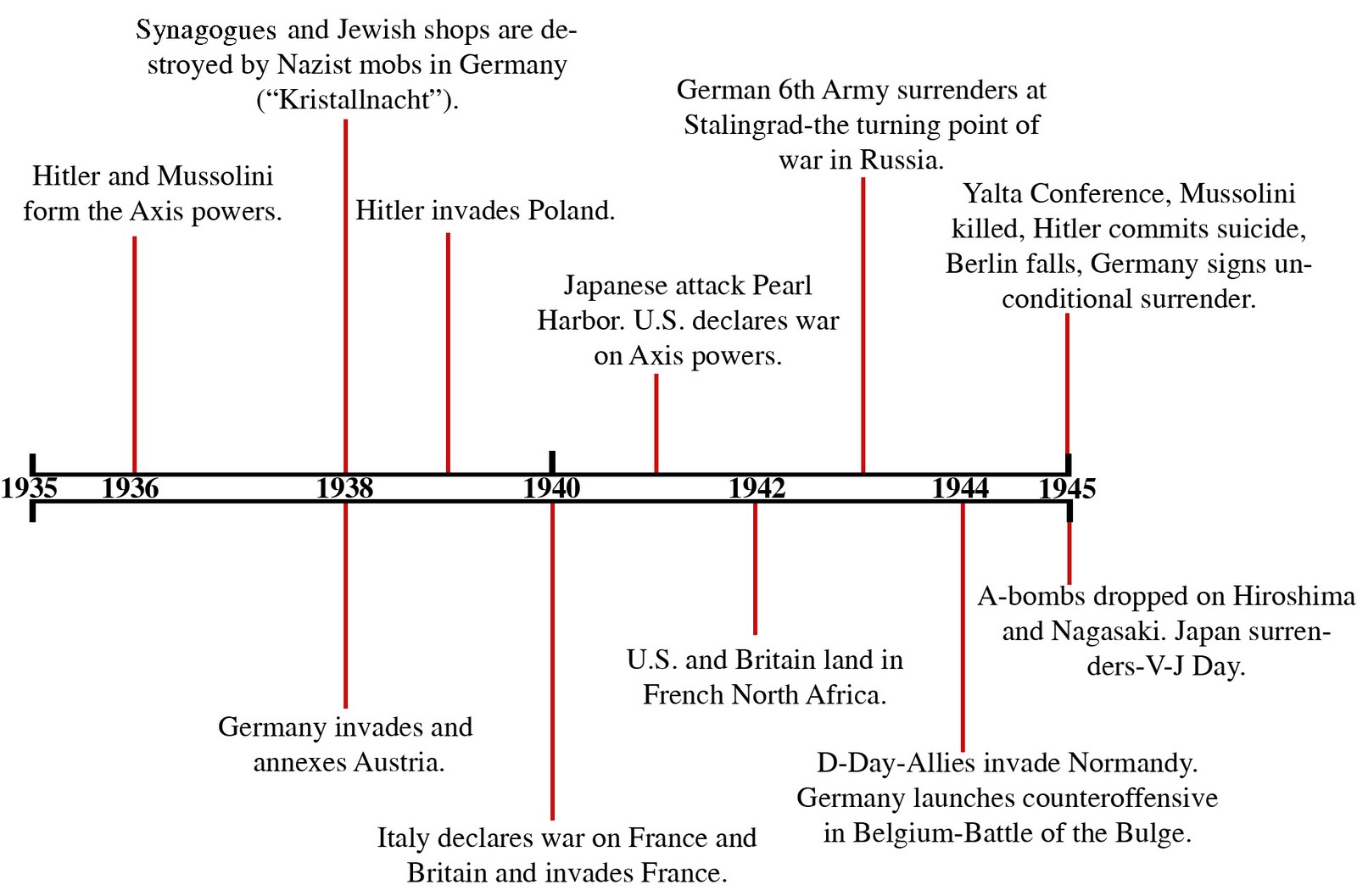
World War II was one of the most significant global conflicts in history, spanning from 1939 to 1945. This war involved many of the world's great powers, which were divided into two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis. Understanding the timeline of events during this tumultuous period is crucial for grasping the complexities of modern history. In this article, we will explore the major events of World War II, detailing the progression of battles, significant political changes, and key developments that shaped the course of the conflict.
As we delve into this timeline, we will highlight pivotal moments such as the invasion of Poland, the attack on Pearl Harbor, and the D-Day landings. Each event played a crucial role in influencing the outcome of the war and the geopolitical landscape that followed. With an emphasis on accuracy and detail, this article aims to serve as a reliable resource for anyone interested in understanding the events that defined World War II.
In addition, we will provide insights and statistics to give readers a clearer picture of the war's impact on different nations and populations. The timeline is organized chronologically, allowing for easy navigation and comprehension of the sequence of events. Let’s embark on this journey through the timeline of World War II and uncover the events that changed the world forever.
Table of Contents
- 1939: The Outbreak of War
- 1940: The Axis Powers Gain Momentum
- 1941: The United States Enters the War
- 1942: Turning Points in the War
- 1943: The Tide Begins to Turn
- 1944: The Allied Invasion of Europe
- 1945: The End of the War
- Conclusion
1939: The Outbreak of War
The year 1939 marks the beginning of World War II, which commenced with the German invasion of Poland on September 1. This invasion prompted Britain and France to declare war on Germany, solidifying the start of the conflict.
Key events in 1939 include:
- September 1: Germany invades Poland.
- September 3: Britain and France declare war on Germany.
- November 30: The Soviet Union invades Finland.
1940: The Axis Powers Gain Momentum
In 1940, the Axis powers made significant territorial gains across Europe. Germany launched a series of successful military campaigns, leading to the fall of several nations.
Key events in 1940 include:
- April 9: Germany invades Denmark and Norway.
- May 10: Germany launches the invasion of France.
- June 22: France surrenders to Germany.
Battle of Britain
The Battle of Britain began in July 1940 and lasted until October. It was a crucial air campaign waged by the German Luftwaffe against the United Kingdom.
- July 10: The battle officially begins.
- September 15: The British Royal Air Force (RAF) achieves a significant victory.
1941: The United States Enters the War
1941 was a pivotal year as it saw the entry of the United States into the war, following the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7.
Key events in 1941 include:
- June 22: Germany invades the Soviet Union in Operation Barbarossa.
- December 7: Japan attacks Pearl Harbor, leading to U.S. entry into the war.
- December 11: Germany and Italy declare war on the United States.
1942: Turning Points in the War
By 1942, the war had reached several crucial turning points, particularly in North Africa and the Pacific.
Key events in 1942 include:
- June 4-7: The Battle of Midway, a major naval battle in the Pacific.
- November 8: Allied forces land in North Africa (Operation Torch).
1943: The Tide Begins to Turn
As the war progressed into 1943, the Allies began to achieve significant victories against the Axis powers, altering the course of the conflict.
Key events in 1943 include:
- January 14-24: The Casablanca Conference, where Allies agree on the next steps.
- July 10: Allied invasion of Sicily.
- November 28-December 1: The Tehran Conference, where Allied leaders plan future strategies.
1944: The Allied Invasion of Europe
In 1944, the Allies launched significant operations to liberate occupied territories in Europe, culminating in the D-Day invasion.
Key events in 1944 include:
- June 6: D-Day: Allied forces land on the beaches of Normandy, France.
- August 25: Paris is liberated from German occupation.
1945: The End of the War
The final year of the war witnessed the defeat of the Axis powers and the subsequent end of World War II.
Key events in 1945 include:
- April 30: Adolf Hitler commits suicide.
- May 7: Germany surrenders unconditionally.
- August 6 and 9: The U.S. drops atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
- September 2: Japan formally surrenders, marking the end of World War II.
Conclusion
World War II was a complex and multifaceted conflict that involved numerous countries and resulted in significant changes to the global order. The timeline of events presented in this article highlights the crucial moments that defined the war and its aftermath.
As we reflect on these events, it is essential to remember the lessons learned and the importance of peace in today's world. We encourage readers to share their thoughts in the comments, explore further articles on our site, and engage with the rich history of World War II.
Thank you for taking the time to read this comprehensive overview of the timeline of World War II. We hope you found it informative and engaging, and we look forward to welcoming you back for more insightful content!
Article Recommendations